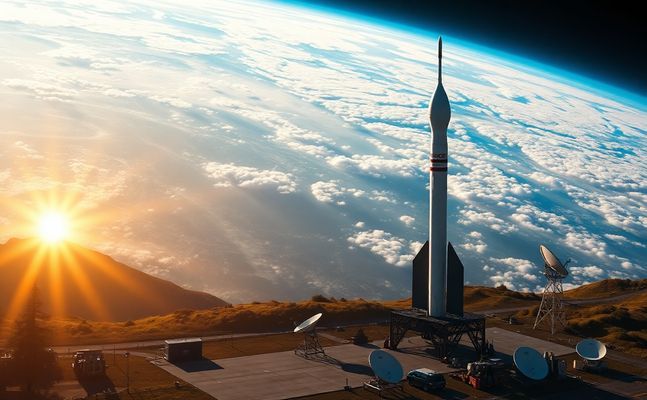
RocketLab’s flight operations have consistently showcased their capability to deliver on their promises. With its innovative use of 3D printing technology and a streamlined manufacturing process, RocketLab has minimized the costs associated with traditional rocket production while maximising payload capacity.
Their dedicated launch facility in New Zealand has facilitated numerous successful missions, thereby affirming RocketLab's commitment to advancing space exploration. However, as the competition intensifies with the likes of SpaceX and others entering the small satellite launch market, RocketLab must continuously innovate to maintain its foothold.

The looming question for RocketLab and its stakeholders revolves around the sustainability of its business model in a saturated market. Companies are increasingly looking for more than just launch services; they seek partners who can offer a comprehensive suite of solutions, including ground support and in-orbit operational services. By refining their contract terms and expanding their service offerings, RocketLab can further entrench itself as a leader in the aerospace domain, making every flight count with a focus on customer satisfaction and operational excellence.
The Vital Importance of LEO for Global Connectivity
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) has garnered significant attention in the space race, particularly due to its critical role in global connectivity and Earth observation capabilities. Numerous satellite constellations, like Starlink and OneWeb, have been launched with the aim of providing internet access to remote regions, thereby minimising the digital divide. The increasing reliance on satellite technology for communication and observation necessitates efficient launch vehicles like RocketLab’s Electron rocket that can operate on a frequent and cost-effective basis.

This focus on LEO not only addresses communication gaps but also serves crucial monitoring and observing functions. Earth observation satellites provide invaluable data for climate change research, disaster management, and agricultural monitoring. In this context, the international community must recognise the importance of investing in LEO satellite technologies that can enhance our understanding of the planet and equip us to respond to environmental challenges effectively.
However, with great opportunity also comes significant challenges. The growing number of satellites in LEO raises concerns about space debris and orbital congestion. It is essential for companies like RocketLab and others in the industry to adopt sustainable practices that ensure responsible end-of-life management for satellites. This could include deorbiting strategies or incorporation of robotic technologies that could help remove defunct satellites from orbit. Thus, the regulatory framework around LEO operations must evolve to safeguard this vital area of space for future generations.
The Role of Robotic Technologies in Modern Rocketry

Robotic technologies have become integral to the advancement of rocketry and space exploration. The precision and reliability of robots in the context of launching and managing payloads offer substantial benefits. RocketLab’s ongoing investment in robotic technologies aims to amplify operational efficiencies and enhance safety protocols during launches and satellite deployment. By automating various processes, from pre-launch checks to in-orbit manoeuvres, RocketLab can improve mission success rates while lowering costs. Furthermore, the application of robotics extends beyond launching; post-launch missions can rely on robotic capabilities for satellite tuning and maintenance in orbit.
Additionally, robotic systems can play a pivotal role in future missions that aim to establish human presence on other celestial bodies, such as the Moon or Mars. Early missions may rely heavily on autonomous robotic systems to prepare the environment for human arrival, including constructing habitats, deploying power systems, and conducting scientific research autonomously. The integration of robotics into space exploration thus not only enhances mission capability but also provides a basis for sustainable human exploration of outer space.

However, as we incorporate more robotic technologies into our systems, it is essential to consider ethical implications and the parameters of human-robot collaboration. The future of the space race may hinge on striking a balance between utilising automation while ensuring that human expertise remains at the forefront of decision-making processes. Thus, as RocketLab and its peers build and deploy more sophisticated robotic systems, fostering public and stakeholder trust in these technologies remains a critical aspect of their long-term vision.
The Current State of Contracts in the Aerospace Industry
The contractual landscape within the aerospace industry, particularly concerning satellite launches and space exploration, continues to evolve in response to changing market demands and competitive pressures. The nature of contracts in this field is shifting towards greater flexibility and bespoke offerings that cater to satellite operators' specific needs. RocketLab, with its recent series of contracts, illustrates how aligning business models with customer requirements can yield mutually beneficial outcomes.
Moreover, as the industry witnesses a growing interest in public-private partnerships, collaboration among government agencies, private firms, and academic institutions is becoming increasingly commonplace. These partnerships often bring together resources, expertise, and funding mechanisms that propel advancement in technology and increase accessibility to space. The nuanced interplay between these entities necessitates a robust contractual understanding that addresses issues such as intellectual property rights, liability, and operational responsibilities.
In this transitional phase, it is crucial for companies like RocketLab to remain agile and proactive in renegotiating and formulating contracts that reflect not only current technological capabilities but also the evolving regulatory environment. As the space race accelerates, companies that can adapt to these dynamics while maintaining transparency and trust will succeed in forging long-lasting relationships with clients and stakeholders. The transformative era of space exploration is upon us, and with it, an opportunity to redefine how we approach contracts and collaborations within the sector.
Fun Facts About RocketLab and the Space Race
As we explore the fascinating world of rocket technology and space exploration, there are many quirky and interesting facts to learn. Did you know that RocketLab’s Electron rocket is named after a phenomenon in quantum physics, highlighting the company's foundation in innovation and technology? Furthermore, each Electron rocket can launch up to 150 kg of payload to a 500 km orbit, showcasing its reliability and efficiency.
Moreover, RocketLab's innovative use of 3D printing means they can create rocket components in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods. On the fun side, RocketLab has made headlines for their creative names for payloads, with some being inspired by pop culture, including “It’s Business Time,” inspired by a popular Flight of the Conchords song. Additionally, the rapid growth of LEO satellite constellations will surpass 1000 satellites by 2025, opening endless possibilities for data collection and global interconnectedness. As we continue to witness these advancements, that push the boundaries of what's possible in the cosmos, the sky is truly no longer the limit.
```

 EN
EN  MT
MT  DE
DE  FR
FR  ES
ES  IT
IT 