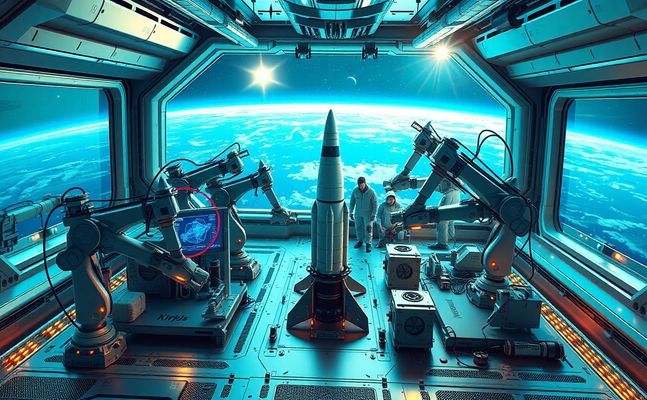
In recent years, the realm of 3D printing has emerged as a transformative force across various industries. However, its implications in space exploration and aviation are particularly noteworthy. With the increasing demand for complex structures in spacecraft and rockets, the potential of 3D printing to innovate and streamline production processes is unparalleled.
Traditional manufacturing methods often fall short when it comes to the geometrical complexities and material requirements of advanced space vehicles. By embracing 3D printing technology, aerospace companies can overcome these limitations, creating lighter and more efficient designs that were previously deemed impossible. Moreover, the ability to rapidly prototype parts enables engineers to test and iterate designs more effectively, expediting the development of new technologies that could lead to significant breakthroughs in our ability to explore space.
3D Printing in Rocket Manufacturing
Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have begun to harness the power of 3D printing for the creation of rocket components. This not only reduces production times but also cuts costs dramatically. For instance, the manufacture of fuel injectors and combustion chambers through 3D printing has enabled these companies to achieve more intricate designs that enhance performance and fuel efficiency. Such advancements are crucial as we aim for more sustainable space travel, reducing waste and minimising the environmental footprint of rocket launches. The use of additive manufacturing allows engineers to develop complex geometries that efficiently manage the extreme conditions of rocket propulsion, ultimately leading to successes in launch missions and payload efficiency. As we witness an increase in private sector involvement in space exploration, the industry is poised on the brink of a manufacturing renaissance driven by 3D printing technology.
Video: Revolutionizing Space 3D Printed Miniature Rocket Engines
The Future of Space Habitats and 3D Printing
As humanity sets its sights further into the cosmos, the prospect of establishing colonies on other planets, such as Mars, brings forth the necessity of innovative building techniques. 3D printing stands out as a viable solution for constructing habitats in the hostile environments of extraterrestrial landscapes. NASA and various aerospace organizations are exploring the use of in-situ resources, such as Martian soil, to print structures that can withstand the planet's conditions. This approach not only provides a means to construct habitats but also reduces the need to transport heavy building materials from Earth, significantly lowering the cost of interplanetary missions. As research and trials continue, the idea of 3D-printed habitats could become a reality, offering astronauts and future colonists robust shelter and vital infrastructure for long-term habitation. The implications of this technology extend beyond mere construction; they represent a foundational shift in how we think about living and working in space.
Observational Science Powered by 3D Printing

Beyond rocket manufacturing and habitat construction, 3D printing is increasingly impacting observational science. Telescopes and satellite components can be redesigned using additive manufacturing techniques to enhance their functionality and effectiveness. For example, 3D-printed instruments allow for the creation of custom optical components that may not be feasible with traditional manufacturing methods.
These advanced technologies enable scientists to develop next-generation telescopes with improved resolution and capabilities for deep-space observation. With missions like the James Webb Space Telescope revolutionising our understanding of the universe, the integration of 3D printing into scientific instrumentation device design becomes even more significant. Consequently, as space observation and exploration advance, so too does the importance of innovative manufacturing techniques to keep pace with scientific curiosity and discovery.
The Current State and Future Goals in 3D Printing for Space Exploration
The landscape of 3D printing in the context of space exploration is rapidly evolving. Current projects focus on creating more complex and efficient systems that push the boundaries of what is technically possible. Organizations around the world are actively conducting tests and developing new applications of 3D printing technology. The goal is to streamline workflows, reduce costs, and enhance the sustainability of missions to explore distant planets and beyond.
As regulatory frameworks adapt and new partnerships emerge between agencies and private companies, the opportunity to achieve unprecedented advancements in space exploration becomes an achievable goal. Future developments may include collaborations to build entire spacecraft directly in orbit, thus paving the way for limitless possibilities in space travel. The continuous innovation in 3D printing technology promises to keep humanity's aspirations for exploration well within reach.
Fun Facts about 3D Printing, Space, and Aviation
Delving into the nexus of 3D printing and space exploration unveils a host of fun facts that spotlight the ingenuity behind these advancements. Did you know that the first 3D-printed object sent to space was a part manufactured by NASA in

 EN
EN  MT
MT  DE
DE  FR
FR  ES
ES  IT
IT 